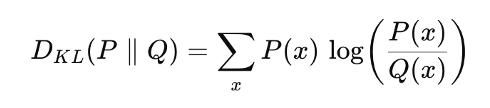KL Divergence
Essential AI Math Excel Blueprints
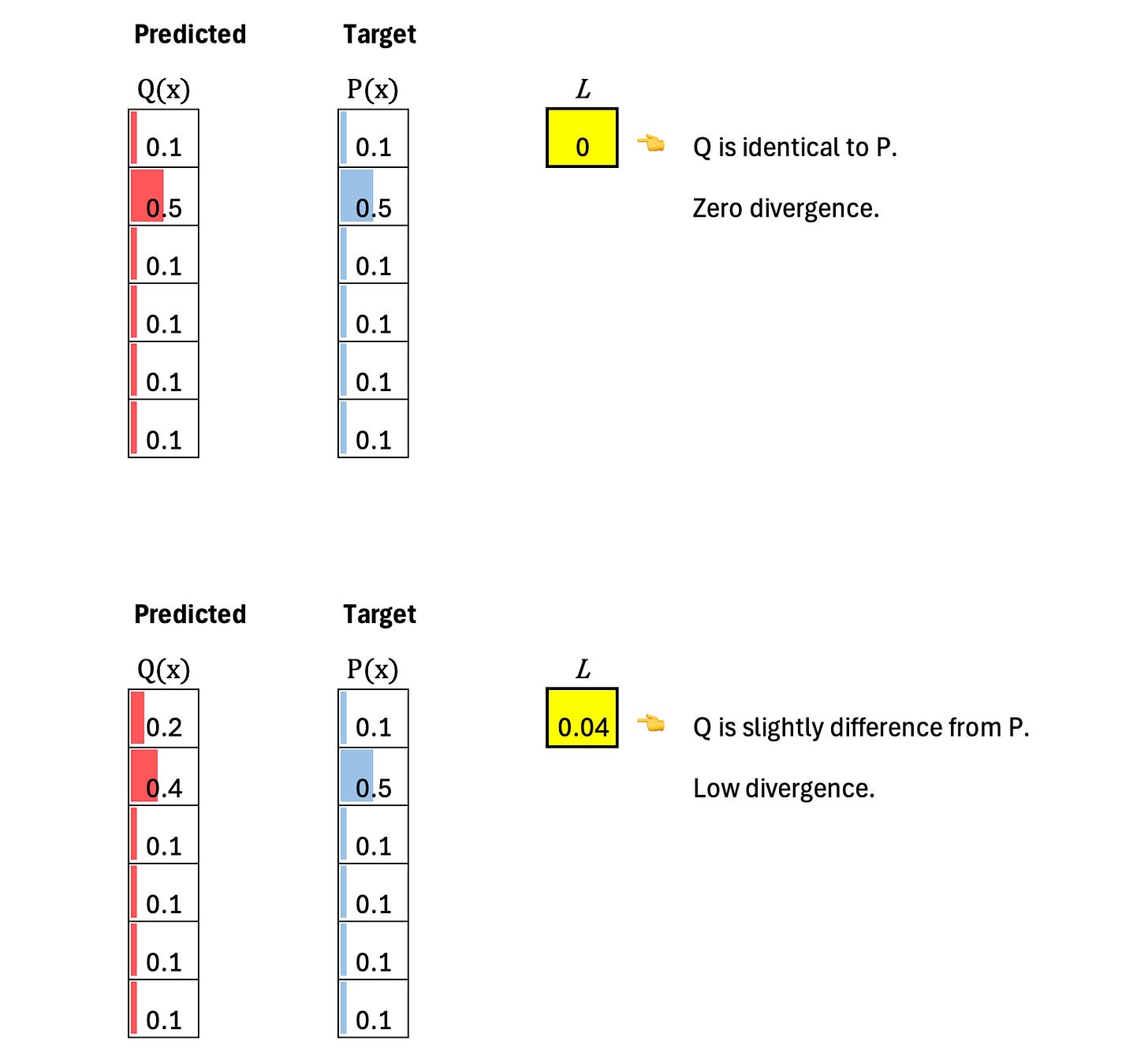
Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence measures how different one probability distribution is from another. It quantifies how much information is lost when we use a model (predicted) distribution (Q) to approximate a true (target) distribution (P).
Calculation
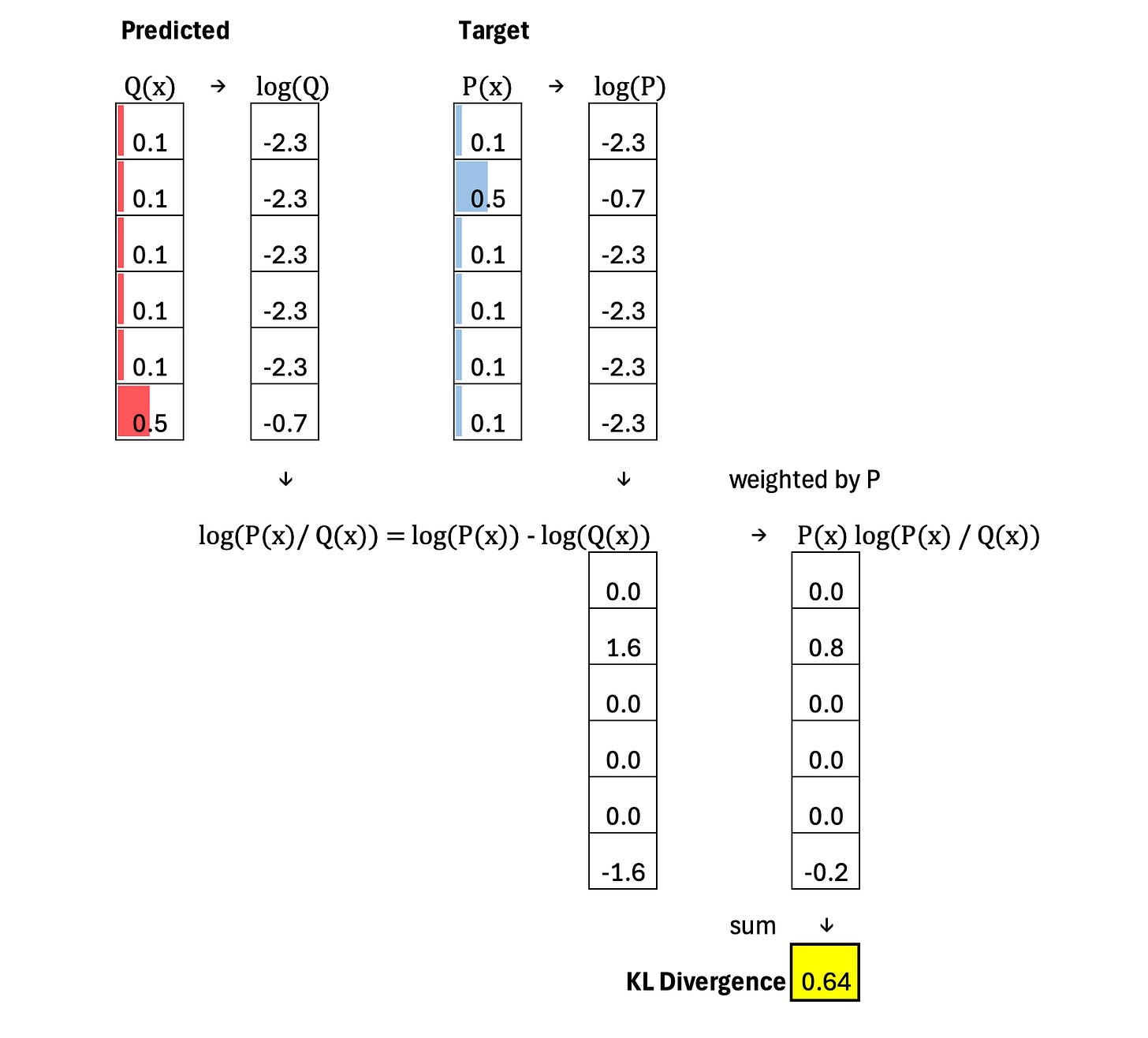
The calculation begins with the predicted distribution Q(x) and the target distribution P(x). First, we take the logarithm of both Q(x) and P(x). Next, for each outcome, we compute the difference log(P(x)) minus log(Q(x)), which represents the log ratio between the target and predicted probabilities. This difference is then weighted by P(x), producing the term P(x) multiplied by log(P(x) over Q(x)). Finally, we sum these weighted terms across all outcomes to obtain the KL divergence.
Excel Blueprint
This Excel Blueprint is available to AI by Hand Academy members. You can become a member via a paid Substack subscription.