L2 Norm
Essential AI Math Excel Blueprints
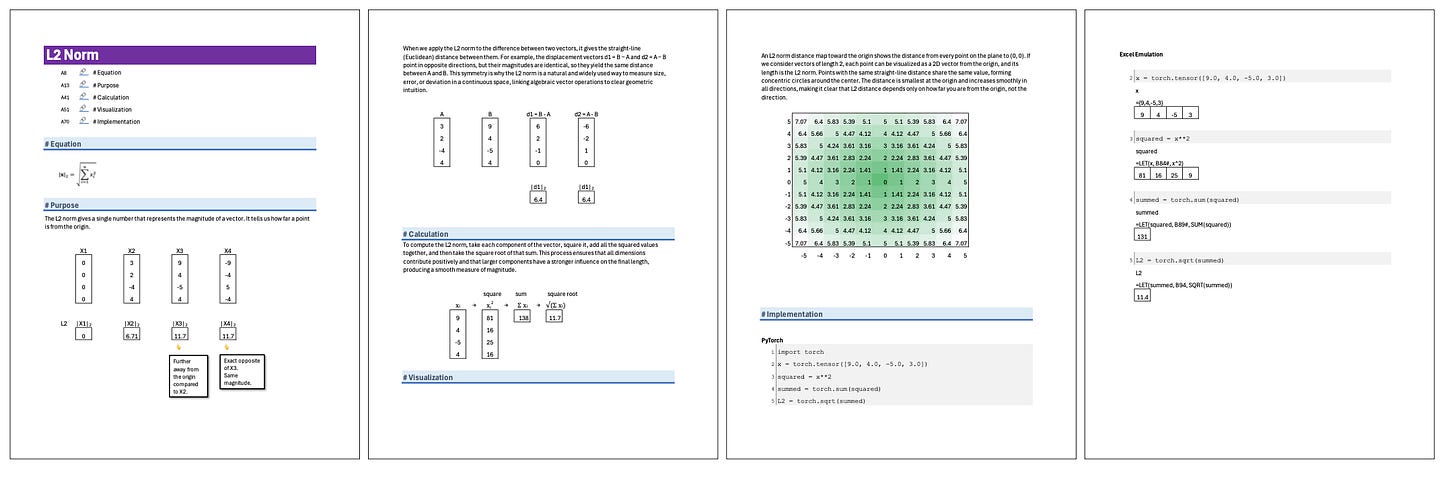
\(\| \mathbf{x} \|_2 = \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{n} x_i^2}
\)
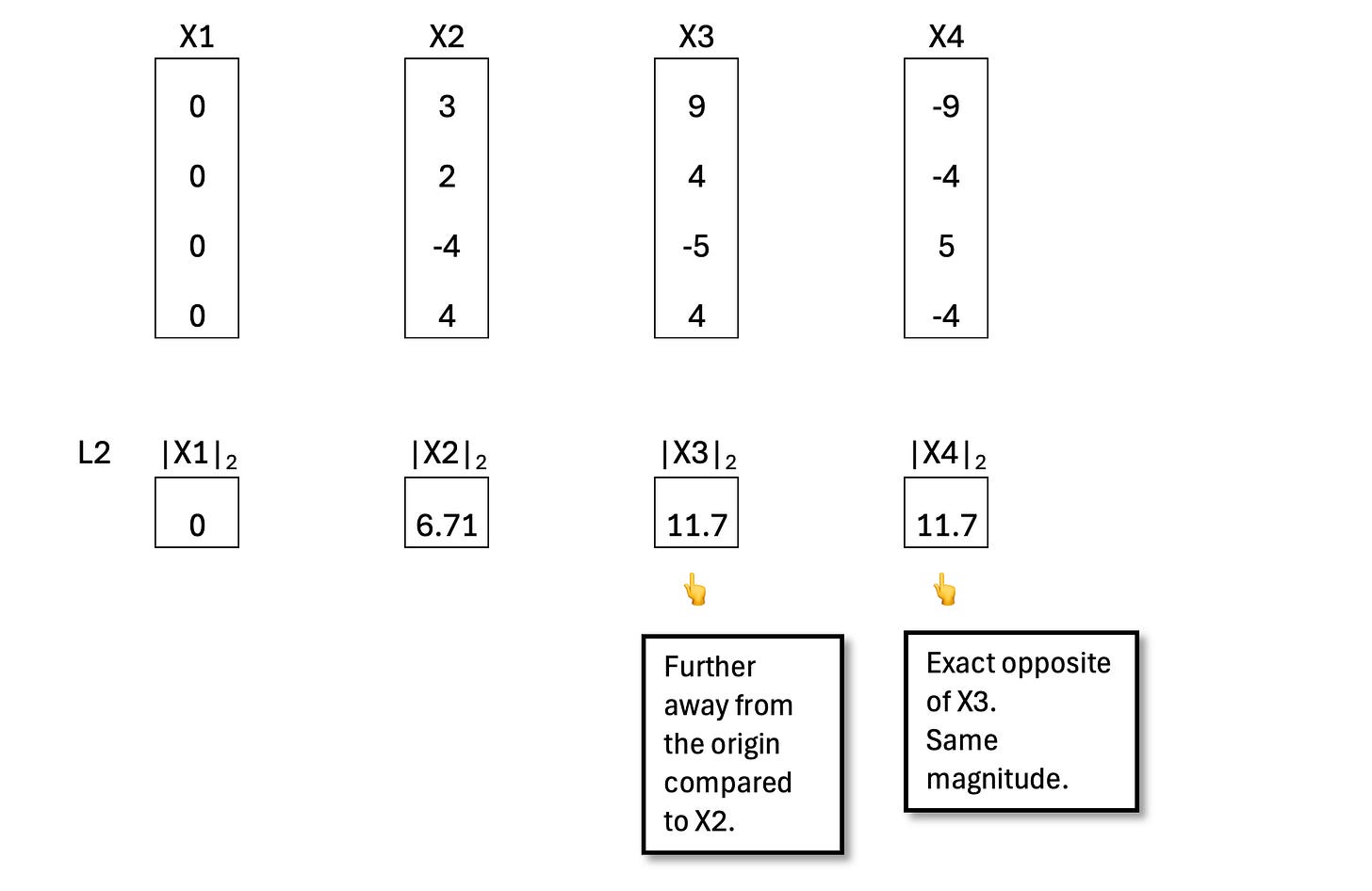
The L2 norm gives a single number that represents the magnitude of a vector. It tells us how far a point is from the origin.
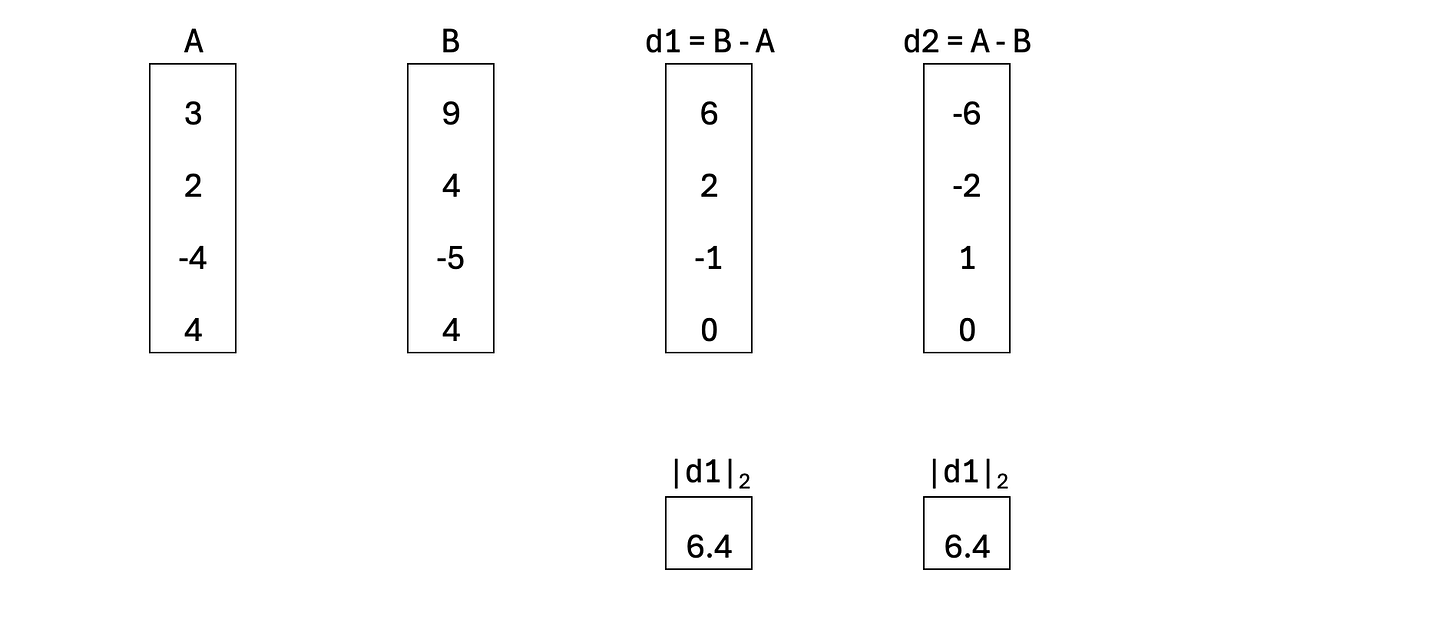
When we apply the L2 norm to the difference between two vectors, it gives the straight-line (Euclidean) distance between them. For example, the displacement vectors d1 = B − A and d2 = A − B point in opposite directions, but their magnitudes are identical, so they yield the same distance between A and B. This symmetry is why the L2 norm is a natural and widely used way to measure size, error, or deviation in a continuous space, linking algebraic vector operations to clear geometric intuition.
Excel Blueprint
This Excel Blueprint is available to AI by Hand Academy members. You can become a member via a paid Substack subscription.