RMS Normalization
Essential AI Math Excel Blueprints
\(\begin{align}
\mu^{(i)} = \frac{1}{D} \sum_{j=1}^{D} x_{j}^{(i)}
\\
\sigma^{2^{(i)}} = \frac{1}{D} \sum_{j=1}^{D} \left(x_{j}^{(i)} - \mu^{(i)}\right)^2
\\
\hat{x}_{j}^{(i)} = \frac{x_{j}^{(i)} - \mu^{(i)}}{\sqrt{\sigma^{2^{(i)}} + \epsilon}}
\\
y_{j}^{(i)} = \gamma_j \hat{x}_{j}^{(i)} + \beta_j
\\
\end{align}\)
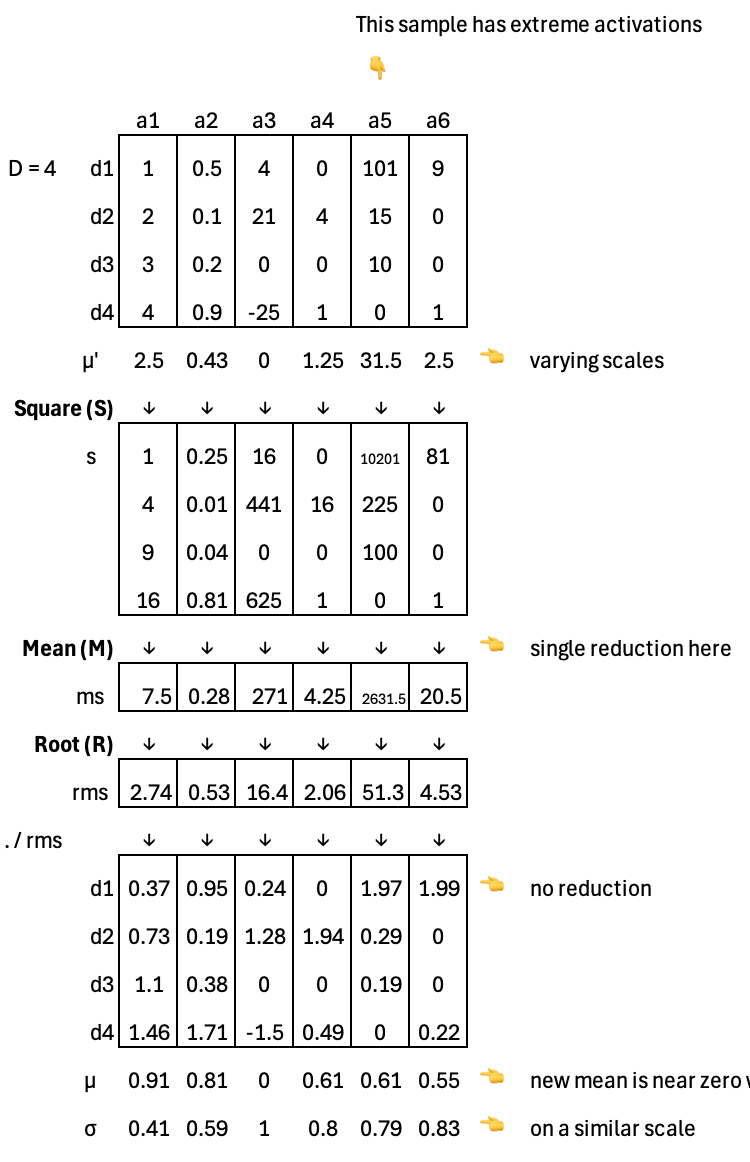
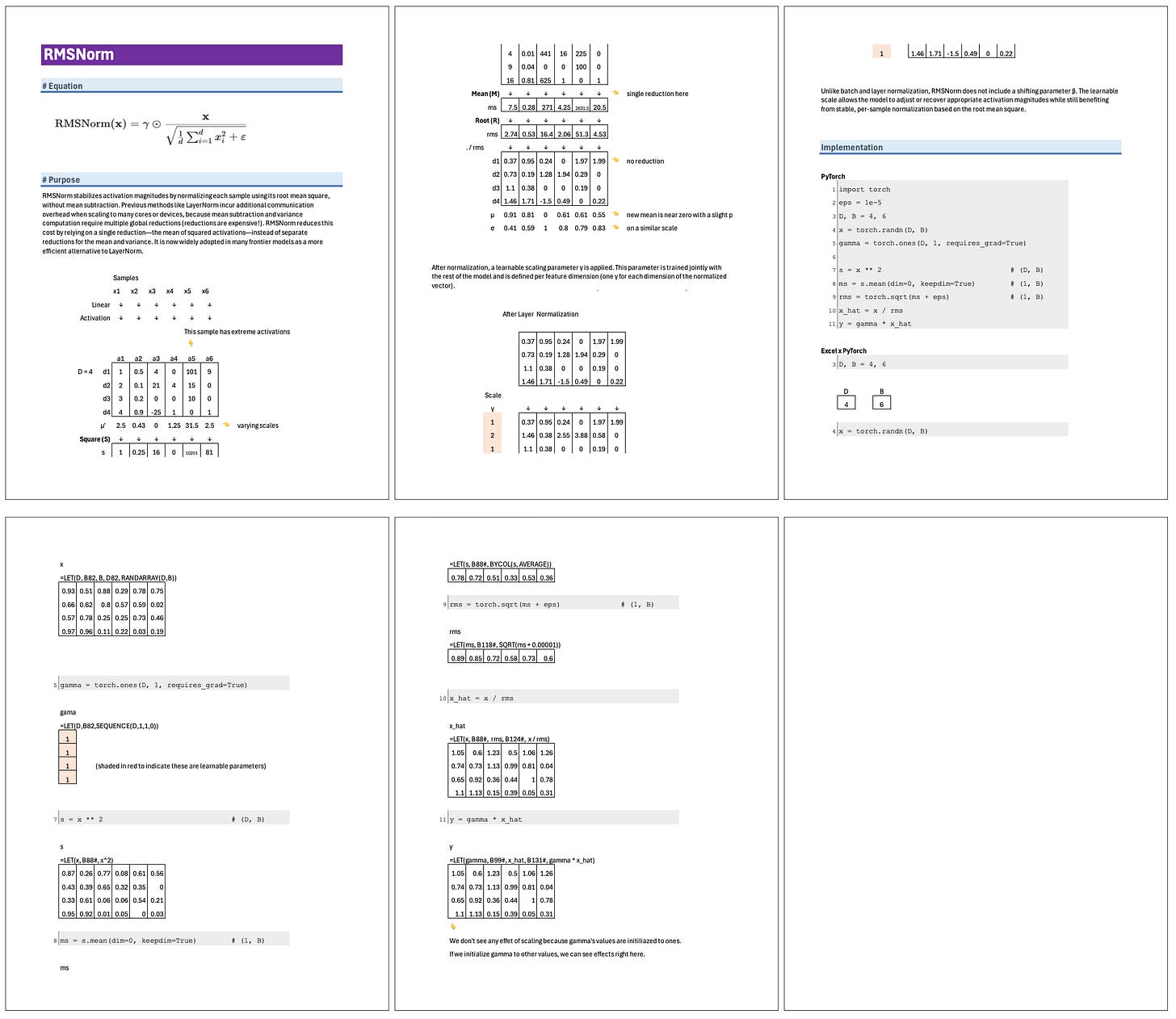
Root-Mean-Square Normalization (RMSNorm) stabilizes activation magnitudes by normalizing each sample using its root mean square, without mean subtraction. Previous methods like LayerNorm incur additional communication overhead when scaling to many cores or devices, because mean subtraction and variance computation require multiple global reductions (reductions are expensive!). RMSNorm reduces this cost by relying on a single reduction—the mean of squared activations—instead of separate reductions for the mean and variance. It is now widely adopted in many frontier models as a more efficient alternative to LayerNorm.
Excel Blueprint
This Excel Blueprint is available to AI by Hand Academy members. You can become a member via a paid Substack subscription.